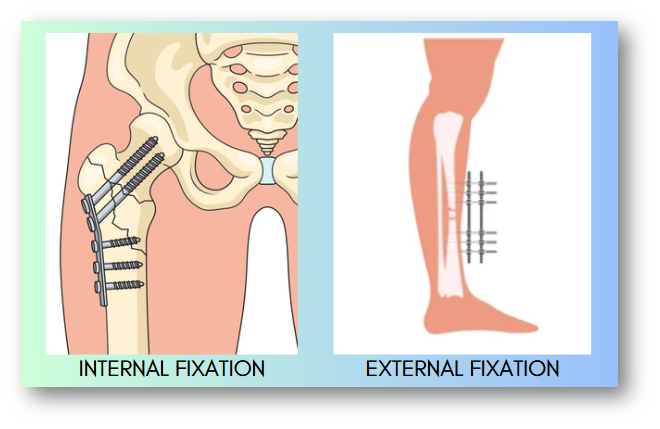
For the treatment of bone fractures, two common methods of stabilization are used: external fixation and internal fixation.
Both of these methods are critical for orthopedic surgeons to ensure better results for the patients. A thorough understanding of the rehabilitation timelines can contribute to making an informed decision for the delivery of the desired patient care.
In this article, we shall discuss both fixation methods in detail by dividing them into their definition, application, and recovery timelines. This information serves as a guide to make a decision that aligns with the specific needs of their patients individually.
What is Internal Fixation Surgery?
Internal fixation surgery is performed to repair the broken bones by realigning
and stabilizing them in the correct position internally. These affected bones
are properly stabilized and supported till the time they are properly healed to
bear the person’s body weight without any discomfort. The types of orthopedic
equipment used for ensuring a successful internal fixation surgery
are - intramedullary interlocking nails,
orthopedic plates, and screws.
The most common types of fractures that are treated using the internal fixation method include:
-
Comminuted fracture
-
Compound fracture (Open fracture)
-
Displaced fracture (in these cases, the pieces of bone move away from each other to form a gap)
-
Joint fractures
-
Spinal stabilization
The majority of surgeons prefer this method because:
-
It allows shorter hospital stays
-
There is a reduced chance of nonunion (incomplete healing) and malunion (incorrectly positioned bone healing) of broken bones
-
It allows patients to restore and regain their normal functions quicker
-
creates a stable condition for the patient for earlier mobilization and weight-bearing activities
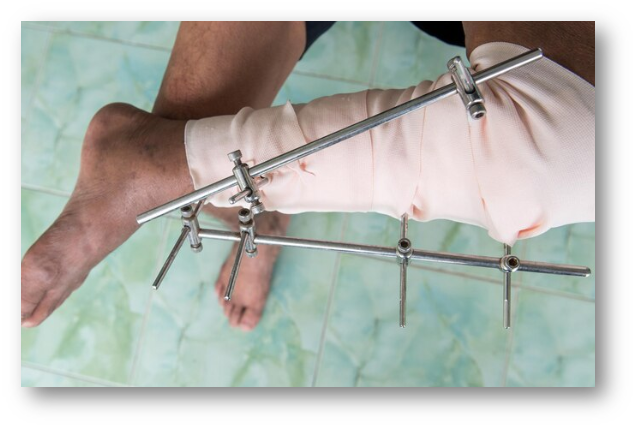
What is an External Fixation Method?
External fixation is an orthopedic surgical procedure used for the optimal alignment and stabilization of fractured bones with the help of an external fixation device placed outside the body. The device is connected to the affected bone through orthopedic pins, wires, and screws.
The main indications of the external fixation method are:
-
Bone fractures with excessive soft tissue swelling
-
Unstable pelvic ring injuries
-
Comminuted periarticular fracture
-
Infected nonunions and malunions
-
Soft tissue reconstruction
-
Genetic bone deformity correction
-
Severe bone loss
-
Limb lengthening
Orthopedic surgeons consider the external fixation method in various cases because:
-
An external fixation protects the surrounding soft tissue from injury during treatment
-
It can be applied quickly to stabilize fractures and even develop bone-related deformities
-
Preferred in cases where infection risk is higher, such as in diabetic foot ulcers
-
Excellent approach for limb lengthening and deformity correction
What Are the Key Factors That Impact the Recovery Process after Orthopedic Surgery?
-
Patient’s Age: As aging happens, the capacity for healing in an individual decreases. It is why older patients are always at risk of complications after fracture treatment.
-
Comorbidities: Diseases like arthritis, diabetes, or any auto-immune disease can degrade the healing process.
-
Medication Usage: A few medicines, such as corticosteroids and NSAIDs, intervene in bone healing and increase the chances of non-union.
-
Fracture Type and Severity: The complexity of the fracture (e.g., comminuted, displaced) significantly impacts healing time and recovery outcomes.
-
Surgical Technique: Recovery time and results can be influenced by the surgeon's ability and the fixation technique's accuracy.
-
Rehabilitation and Patient Compliance: Staying adherent to the physical therapy and postoperative care instructions provided by surgeons plays a major role in accelerating recovery and also promises better results.
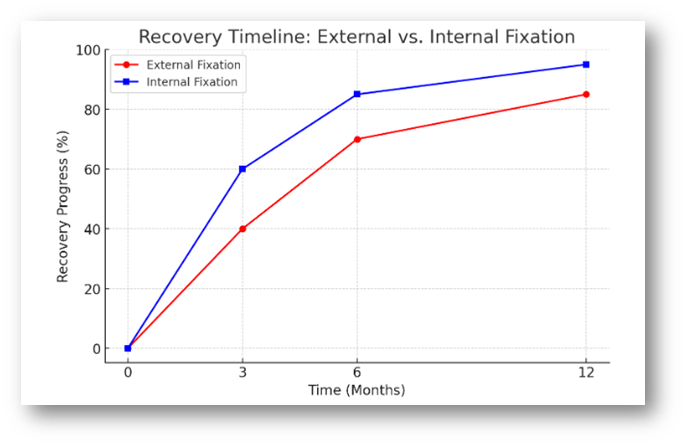
Comparative Analysis of Recovery Timelines of Internal and External Fixation
Analyzing the recovery periods for internal and external fixation offers important information about the healing mechanisms involved in each technique. Although both methods fix fractures, they use different approaches, affecting rehabilitation.
Initial Recovery Phase (0-3 months)
The early recovery period for both surgical techniques lasts for the first three months. Every phase impacts various aspects of a patient’s life differently.
| Attributes |
Internal Fixation |
External Fixation |
| Activity Level |
The patient can move freely without limitation; even the physical therapy begins sooner.
|
Restrained activity, as there is a completed focus on healing and bone alignment.
|
| Focus |
Restoring and regaining strength of fractured bone.
|
Wound care and infection monitoring are crucial in this case because they are performed mainly in patients with higher infection risk.
|
| Functional Results |
Early mobility is easy to attain; thus, the functional results are always better.
|
There is a delay in reviving joint mobility and grip strength.
|
| Potential Complications |
There is a lower risk of complications because the technique is performed in individuals with healthier daily lifestyles and habits.
|
There is a higher risk of minor complications, such as pin site infections, in immunocompromised patients.
|
Intermediate Recovery Phase (3-6 months)
| Attributes |
Internal Fixation |
External Fixation |
| Functional Outcomes |
Better outcomes, as there is improvement in the ability to move, with an increasing range of motion and enhanced grip strength
|
Delay in the grip strength and overall joint functioning
|
| Mobility |
Significant boost in mobility due to the stabilized orthopedic implants, such as plates, nails, and screws
|
Restriction due to the external frame, but gradual improvement is noticeable steadily
|
| Rehabilitation Focus |
Extensive physical therapy that aims at increasing strength for performing daily activities
|
Managing the remaining discomfort while gradually increasing activity levels
|
| Patient Experience |
Patients report greater satisfaction in these cases due to easier recovery without any restrictions
|
Patients may get irritated due to the inconvenience and limitations caused by the external fixation device
|
| Activity Level |
It helps to resume normal routines quickly and even allows sportspeople to get back on the track earlier
|
Longer time required for resuming normal activities
|
| Risks Associated |
There is a lesser risk of complications; however, too much physical exertion on treated bone can hamper recovery.
|
The risk of complications is higher due to infections and external elements.
|
Final Recovery Phase (6-12 months)
| Attributes |
Internal Fixation |
External Fixation |
| Device Removal |
These orthopedic devices stay intact to the bone and are not removed unless there is a medical complication caused by it
|
The majority of the patients will have their external fixation device removed by this time
|
| Mobility |
Patients achieve significant improvement in mobility and function
|
A few patients with diseases like foot ulcers might still experience trouble with mobility and stiffness
|
| Recovery Duration |
The healing process is completed, which allows for quicker recovery
|
Potential issues like delayed or malunion may cause full recovery to take longer.
|
| Functional Outcomes |
The majority of people can resume their regular activities and sports.
|
Because of past medical issues, patients may have trouble reaching optimal function.
|
| Rehabilitation Focus |
Patients often continue therapy to maintain strength and flexibility, enjoying fewer restrictions.
|
Ongoing rehabilitation is essential to help regain full function and adapt to any residual limitations.
|
Clinical Cases and The Right Fixation Method for Them
External Fixation:
-
Soft Tissue Damage: Ideal for severe soft tissue injuries.
-
Open Fractures: Promotes wound care and easy access to infection control in patients with pre-existing conditions.
-
Temporary Stabilization: Used for short-term fracture management.
Internal Fixation:
-
Closed Fractures: Best for precise bone alignment.
-
Weight-Bearing Bones: Suitable for high-load bones like the femur or tibia.
-
Early Mobilization: Enables faster rehabilitation and recovery.
Sharma Orthopedic: Promise Quality Production of Implants for Proper & Faster Recovery
We at Sharma Orthopedic ensure that our highly advanced manufacturing processes and multilayered quality control assist in streamlining the recovery process. As a trusted orthopedic implant manufacturer, we aim to ensure that recovery is not delayed or hampered due to any quality-related issue.
Our certifications from the country’s authorized organizations prove our product quality. They also promise a comfortable and convenient healing after the surgical placement of our implants.
-
Certified for the ISO 13485 and ISO 9001-2015 along with WHO-GMP and Indian FDA (CDSCO)
-
Implement the recent technology for superior and highly compatible implant design
-
Provide stability and minimize implant failure risks
-
Ensure seamless integration of implants with the human body
Final Thoughts
Overall, one can conclude that both internal and external fixation have different effects on every aspect of the patient during their recovery timeline. Many factors decide the entire journey of healing, soft tissue preservation, and mobility for patients.
Orthopedic surgeons must assess each case in a specific way to optimize patient outcomes. Being updated with the latest advancements in orthopedics will improve surgical accuracy and patient recovery.